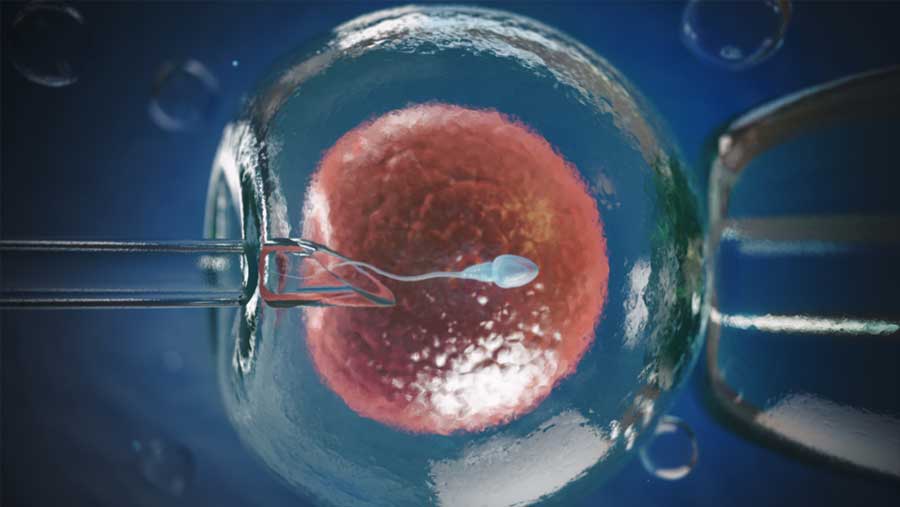
A set of intricate treatments known as in vitro fertilisation (IVF) are used to help with fertility, prevent genetic issues, and aid in child conception.
In IVF, mature eggs are removed from ovaries and fertilized in a laboratory using sperm. The fertilized egg (or eggs) is/are then transported to a uterus. IVF cycles are completed in roughly three weeks. When these processes are divided into separate sections, the process might sometimes take longer.
The most successful type of assisted reproductive technology is IVF. The process is possible with the use of the couple’s own sperm and eggs. A known or unknown donor’s eggs, sperm, or embryos may also be used during IVF. A gestational carrier, a woman who has had an embryo implanted in her uterus, may occasionally be employed. Infertility or genetic issues are treated by in vitro fertilisation (IVF). If intrauterine insemination (IUI) is used to treat infertility, you and your partner may be able to try less invasive treatment options before attempting IVF, such as fertility medications to boost egg production or IUI, in which sperm are placed directly in the uterus close to the time of ovulation.
IVF is occasionally recommended as the first line of therapy for infertility in women over the age of 40. If you have specific medical issues, IVF may still be an option.

What Infertility Causes Can IVF Treat?
- Endometriosis
- Endometriosis
- Low Levels of Sperm
- Issues with the Fallopian Tubes or Uterus
- Difficulties with Ovulation
- Issues with Antibodies That Impair Sperm Or Eggs
- The Incapacity Of Sperm To Survive Or Pass Through Cervical Mucous
- Poor Quality Eggs
- Genetic Disorder In The Father Or Mother
- A Mysterious Reproductive Issue